Views: 69 Author: Site Editor Publish Time: 2023-03-16 Origin: Site
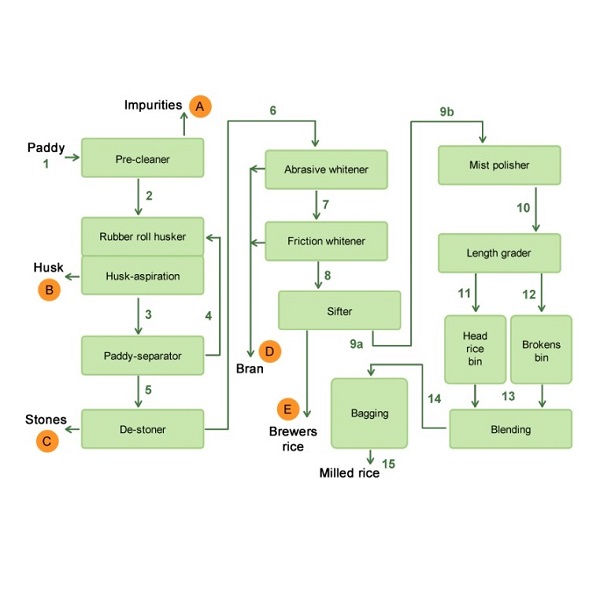
The flow diagram below represents the configuration and flow in a typical modern rice mill.
1 - paddy is dumped in the intake pit feeding the pre-cleaner
2 - pre-cleaned paddy moves to the rubber roll husker:
3 - mixture of brown rice and unhusked paddy moves to the separator
4 - unhusked paddy is separated and returned to the rubber roll husker
5 – brown rice moves to the destoner
6 - de-stoned, brown rice moves to the 1st stage (abrasive) whitener
7 - partially milled rice moves to the 2nd stage (friction) whitener
8 – milled rice moves to the sifter
9a - (for simple rice mill) ungraded, milled rice moves to bagging station
9b – (for more sophisticated mill) milled rice moves to the polisher
10 - Polished rice, will move to length grader
11 - Head rice moves to head rice bin
12 – Brokens moves to brokens bin
13 – Pre-selected amount of head rice and brokens move to blending station
14 – Custom-made blend of head rice and brokens moves to bagging station
15 – Bagged Rice moves to the market
A – straw, chaff and empty grains are removed
B - husk removed by the aspirator
C – small stones, mudd balls etc. removed by de-stoner
D - Coarse (from 1st whitener) and fine (from 2nd whitener) bran removed from the rice grain during the whitening process
E - Small brokens/brewer’s rice removed by the sifter